Continued robust market growth and significant investments
The global market for satellite-based communication continued to grow in 2022. The market continues to be characterized by major investments in new technology and increased capacity, which is driving the industry forward. The more advanced part of the market, which Ovzon addresses, is driven primarily by the need not only for a high degree of mobility and high-speed data transfer but also by security and perfor-mance. The increased security policy concerns resulting from the war in Ukraine are also expected to increase national expenditure for military preparedness, which includes satellite-based communication.
Ovzon operates in the field of satellite-based communica-tion, which is the largest of the three fields that comprise the global space economy. Sales in the part of the field of satellite-based communication that Ovzon addresses were estimated at around USD 21 billion in 2022. In 2023, the addressable market for Ovzon is expected to have USD 22.5 billion in sales, corresponding to 7 percent growth. According to the industry organization NSR, the largest amount of growth in coming years will occur in the field of satellite-based mobile communication.
Ovzon’s addressable market is divided into three segments, which had the following estimated sales in 2023:
• Government agencies and defense forces (USD 7.0 billion);
• mobility services for land, air and marine transportation (USD 7.5 billion); and
• industrial solutions for the media, aid organizations, transportation, mine operation, oil and gas, energy, and the internet of things (USD 8.0 billion).
Ovzon believes that the company’s unique offering is well positioned to meet the needs of the addressable market. The company’s service offers truly mobile communication, meaning small and portable terminals that have secure direct connections and can send/receive at the highest data speeds with guaranteed availability of communication globally.
Ovzon operates in a section of the market known as the advanced satellite connectivity market, which NSR estimates is worth approximately USD 21 billion – according to NSR, a segment with a high rate of growth.
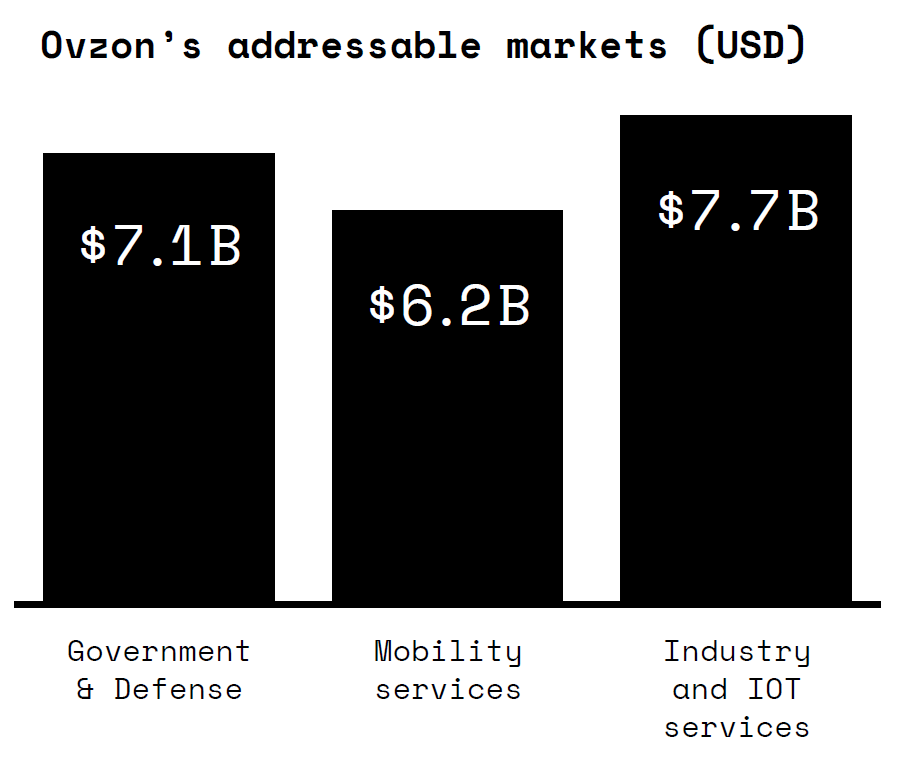
Ovzon’s addressable market is divided between government agencies and defense organizations (USD 7.1 billion), mobility services for land, air and marine transportation (USD 6.2 billion) and industrial solutions (USD 7.7 billion). Solutions that are adapted to the industry consist of media, aid organizations, transportation, mine operation, oil and gas, energy and the internet of things (IoT). Other parts of the satellite connectivity market such as broadband access or broadband internet, are not priorities for Ovzon. Ovzon believes that the company’s unique offering is well positioned to meet the needs of the addressable market: a service with truly mobile communication, meaning small and portable terminals that have secure direct connections and can send/receive the highest data rates with guaranteed availability of communication globally. Other parts of the satellite-based communication market such as broadband access or broadband internet, are neither priorities for nor addressed by Ovzon.
Key market drivers
In the part of the satellite-based communication market that Ovzon addresses, the company believes that the main driver is based on the need for services with a high degree of mobility, high-speed data transfer, and resilience.
From a global perspective, the need for communication in all sectors of society is growing. Stringent demands and expectations are being placed on access to connections with high data rates and mobility, as well as a robust increase in data and content. This requires stable, reliable connections with small, portable communication devices that can transmit large amounts of data regardless of where the users are located – in a city, in areas with insufficient infrastructure, or in the most remote and isolated areas in the world. Moreover, the demand for secure communication is growing. More government organizations and companies are being exposed to hacking and attacks via terrestrial networks that threaten to paralyze operations and government agencies for long periods.
The demand and market for satellite-based communication in 2022 was also impacted by increased geopolitical turbu-lence. This was evident above all in Europe. The invasion of Ukraine and the regional instability it has created is a major concern for most European nations, with expected increases in expenditure for military preparedness as a share of GDP over the next decade. Ovzon 3, in its planned orbital position, is highly suited to meet Europe’s need for robust, resilient, and secure communication. The European market will remain in focus for Ovzon, and additional resources and investments will be targeted at this region in 2023.
The value chain
The market comprises many different operators acting as generalists, integrators, and specialists. This is evidenced by the fact that a small number of satellite operations have significant market shares. Ovzon’s clear strategy and offering create competitive advantages through a strategic balance of important characteristics adapted to the company’s focus on specific customer segments that have stringent requirements that are characterized by unique needs such as mobility, high data rates (both uplink and downlink), a high degree of link accessibility and a high level of security. Ovzon believes competition in this part of the market is limited.
One of Ovzon’s closest competing offerings comes from mobile satellite service (MSS) operators. These services include satellite terminals that are equal in size to Ovzon’s, but with a transmission speed and performance that is significantly lower. There are also competing offerings from high throughput satellite (HTS) operators with satellite-based communication terminals that are somewhat larger but have only the capacity to transmit at lower data rates.
GEO satellite-based communication services
Our competitors’ services are largely based on high-capacity geostationary earth orbit (GEO) satellites. The geostationary earth orbit is a circular orbit on the Earth’s equatorial plane, at a distance where a satellite in this orbit rotates around the Earth in the same direction and with the same orbital period as the Earth’s rotational period. They have been designed to offer the largest possible total accumulated bandwidth in the satellite, equally distributed over a large geographical area. The main competitive advantages of these types of services are coverage area and a price that is often lower. From a mobility perspective, however, this service design has involved clear disadvantages in the form of relatively lower transmission speeds and a need for larger terminals on the ground. They are thus more difficult to manage for mobile solutions, take longer to install and the transmission speed is significantly lower than the one Ovzon offers.
Ovzon’s first satellite – Ovzon 3 – is a leader in the develop-ment of a new generation of GEO satellites and, compared with many other satellites, has more antennas with a larger amount of targeted capacity and energy. It is also largely software-defined, using a unique and proprietary on-board processor (OBP). It can thus be said that the addressable market is being provided with a new type of trailblazing functionality as well as a higher degree of mobility, data rates, and resilience.
Ovzon 3 will thus enable continued innovations of even smaller portable terminals on the ground with higher data rates, unbeatable flexibility and mobility, and built-in security. The development of new types of application that are not currently available in satellite-based communication, such as direct communication between two small satellite-based communication terminals without needing to connect via a teleport/gateway located on Earth and connected to the internet, will also be on offer. This increases protection against disruptions and will result in unbroken communica-tion even if the ground network and other communication alternatives are rendered inoperable. It also reduces delays.
Low Earth Orbit (LEO)-based services
The introduction of services that use, or are intended to use, low earth orbit (LEO) satellites is continuing. LEO satellites are smaller in size, and the business model is based on a larger number of smaller satellites that create a network. For decades, the satellite-based communication industry has sought to develop LEO communication solutions. In recent years, this development has progressed rapidly due to major investments in, for example, companies such as SpaceX with its Starlink satellites. To date, they have launched over 3,600 satellites, of which 2,850 remain operational. Starlink intends to launch 40,000 satellites at an estimated initial cost of approximately SEK 400 billion. Starlink is designed primarily to provide high-speed internet – especially downlink speeds – and initially for the consumer market. The service is targeted above all at consumers who lack access to the internet, and competes primarily with terrestrial internet and 4G/5G.
The Canadian satellite operator Telesat, which is already an established geosynchronous earth orbit (GEO) player, announced several years ago that it intended to launch an LEO network with only around 300 satellites at a cost of around SEK 50 billion. It has now scaled the project back to contain 188 satellites, though at the same investment amount, of which roughly SEK 17 billion remains unfinanced. In parallel, Amazon has initiated Project Kuiper and has applied to launch over 3,000 LEO satellites. It has booked 83 launches, and expects to send up two prototype satellites in 2023. Another project, OneWeb, had sent up 72 satellites through March 2020, when the company went bankrupt. The company re-emerged in late 2020 with newly invested capital and a reconstructed ownership group, and has launched approximately 460 satellites to date; it is unclear how many of them must be replaced with the next generation of satellites. The plan is to send up some 650 satellites in total. In 2022, the satellite operator Eutelsat decided on a merger with OneWeb, with the aim of creating a multi-orbit solution. However, one important aspect – and a potential bottleneck – is access to terminals.
Another LEO company, AST Space Mobile, could potentially be considered to have the most audacious concept from a technological and regulatory perspective. It aims to launch significantly larger LEO satellites into an orbit 700 km above the Earth’s surface that will communicate directly with a regular mobile phone using a high degree of bandwidth and without extra equipment. The company sent up a new proto-type satellite in 2022, successfully unfolding the 64-square meter satellite antenna. Thales, Ericsson, and Qualcom also announced a project that involved testing 5G via LEO.
The strength of GEO presents challenges for LEO
Even though several LEO solutions have made significant progress and are offering their services commercially, many challenges remain. From a historical perspective, achieving profitability in these projects has proven difficult. There are fundamental obstacles that are in part based on the global nature of the LEO systems, and in part to the fact that large portions of the Earth are uninhabited and there are thus very few or no potential paying customers on approximately 90 percent of the Earth’s surface. In parallel, the pace
of continual expansion of the terrestrial communication network is increasing. A number of similar LEO projects were launched in the early 2000s. Some were shut down before launch, while others such as Iridium, Orbcomm, ICO Global Communications and Globalstar later went bankrupt – though some of these, such as Iridium, later re-emerged.
What is often ignored is that the LEO satellites must be replaced more frequently – up to every five years – since they are closer to Earth and are thus more affected by its gravitational pull. These can be compared with GEO satellites, which have a service life of approximately 15 to 20 years. In most cases, the investments referred to in LEO projects thus concern the initial investment.
There are other challenges – such as technical and regula-tory – as well. GEO satellites always have regulatory priority over LEO satellites, which means that LEO satellites have no protection if a disruption occurs.
A certain advantage of the LEO project is lower signal delay due to the satellites’ proximity to Earth. It should be noted, however, that passing through teleports/gateways and other satellites increases signal delay and also creates a risk of hacking.
Add-ons, and potential collaboration and business partners, for Ovzon
As mentioned previously, investments in the LEO segment are considerable, which is driving developments forward both within the segment and for the industry as a whole. This is a positive for the entire satellite-based communication industry and its customers. If any of these projects are realized in accordance with plans, however, these LEO players and their services are an excellent complement and potential partners for Ovzon, which addresses other customer needs. Ovzon is focused on markets, customers, and segments that require guaranteed secure communication capability, which is a supplement to LEO-based consumer services.
Ovzon’s SATCOM-as-a-Service offering is specially designed for the most demanding customers and for difficult environ-ments. The service is used in critical situations where the capacity to provide the highest data rates – both sending and receiving – with the smallest portable terminals and a secure connection are crucial.
Ovzon’s market-leading satellite-based communication service
Ovzon’s choice of basing the company’s unique SATCOM-as-a-Service offering on, and using, GEO satellites has to do with the demands of the company’s customers for high-performance and integrated complete solutions. This means the company is in a unique position and has a brand in the markets it has chosen to operate in. Ovzon has always focused primarily on understanding its customers’ needs and requirements, today and in the future. Accordingly, the technology and innovation are designed and applied to deliver the best integrated products and services.
The market for satellite-based communication continues to attract a great deal of venture capital and major investments via high-quality investors. This drives development rapidly forward and generates continual progress. Ovzon has a strong position as a leader due to the company’s proximity to its customers and its capacity for integrating hardware, software, and satellite-based communication. In combination with the company’s position on the leading edge of tech-nological solutions, this means that the company is highly relevant for the customers and markets that it has chosen to address. Ovzon is the only service provider that furnishes a fully integrated portfolio of products and services for high-performance satellite-based mobile communication.